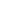Several drugs are available on the market, each with a particular role in treating gout. The information in this article is meant to educate you on the options and their side effects and to guide you in making the appropriate choice. Gout medications work by pursuing specific mechanisms, such as lowering the level of uric acid.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS)
 These are prescribed by doctors as anti-inflammatory medications. They reduce inflammation by inhibiting the actions of certain enzymes and proteins. Aspirin is one of the common NSAIDS in the market but is contraindicated due to its tendency to increased levels of uric acid. NSAIDS may cause adverse side effects if you have other complications such as kidney, liver, or heart diseases. They may also lower iron counts in the blood and cause bleeding in ulcers. Therefore, you should consult with a physician before taking NSAIDS.
These are prescribed by doctors as anti-inflammatory medications. They reduce inflammation by inhibiting the actions of certain enzymes and proteins. Aspirin is one of the common NSAIDS in the market but is contraindicated due to its tendency to increased levels of uric acid. NSAIDS may cause adverse side effects if you have other complications such as kidney, liver, or heart diseases. They may also lower iron counts in the blood and cause bleeding in ulcers. Therefore, you should consult with a physician before taking NSAIDS.
- Colchicine
This medication is effective in relieving the inflammation caused by the formation of crystals. It does not reduce the levels of uric acid. Colchicine prevents future gout attacks and also controls the severity of gout attacks. It is prescribed in high doses for a short period or in low doses for a longer period. This is due to its adverse side effects such as kidney problems, diarrhea, nausea, complications of the bone marrow, and liver issues.
- Corticosteroids
 These are used as anti-inflammatory medications. They are administered on a single joint in tiny doses to minimize its severe side effects. Corticosteroids are used as a last resort when all else has failed. IV infusions are used if the patient is affected in more than a single joint. They are administered in the lowest possible dose and in the shortest period to reduce the effects on the normal production of steroids in the body and the adrenal glands. Its side effects include glaucoma, high blood pressure, cataracts, acne, increased infections, poor healing of wounds, bone loss, moodiness, fluid gain, and weight gain.
These are used as anti-inflammatory medications. They are administered on a single joint in tiny doses to minimize its severe side effects. Corticosteroids are used as a last resort when all else has failed. IV infusions are used if the patient is affected in more than a single joint. They are administered in the lowest possible dose and in the shortest period to reduce the effects on the normal production of steroids in the body and the adrenal glands. Its side effects include glaucoma, high blood pressure, cataracts, acne, increased infections, poor healing of wounds, bone loss, moodiness, fluid gain, and weight gain.
Therefore, they cannot be administered for long term treatment.
- Uricosuric Agents
These medications are effective in removing excess uric acid, by stimulating the kidneys. They are also used to prevent the occurrence of future gout flares. The side effects of uricosuric agents include kidney issues, rash, headaches, and stomach issues.
- Allopurinol
 This is relatively safer when compared to the above medications, and can be administered for a long period of time. It is responsible for preventing the body from producing xanthine oxidase, the enzyme that causes an increase in uric acid. When allopurinol is used for an extended period of time, it helps to lower and regulate the amount of uric acid produced in the body. Its side effects include bone marrow complications, rash, and liver inflammation.
This is relatively safer when compared to the above medications, and can be administered for a long period of time. It is responsible for preventing the body from producing xanthine oxidase, the enzyme that causes an increase in uric acid. When allopurinol is used for an extended period of time, it helps to lower and regulate the amount of uric acid produced in the body. Its side effects include bone marrow complications, rash, and liver inflammation.
Seek the qualified medical advice of a physician before using any of the above medications. You should disclose to your doctor about the history of your medications, health, and possible reactions or side effects from drugs. Most of these gout medications are notorious for producing severe complications and should be taken with utmost care and precision. Your doctor should also recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Do you want to find an effective Gout treatment? Check out our top rated Gout products